Common Activation Functions in Machine Learning
Tags
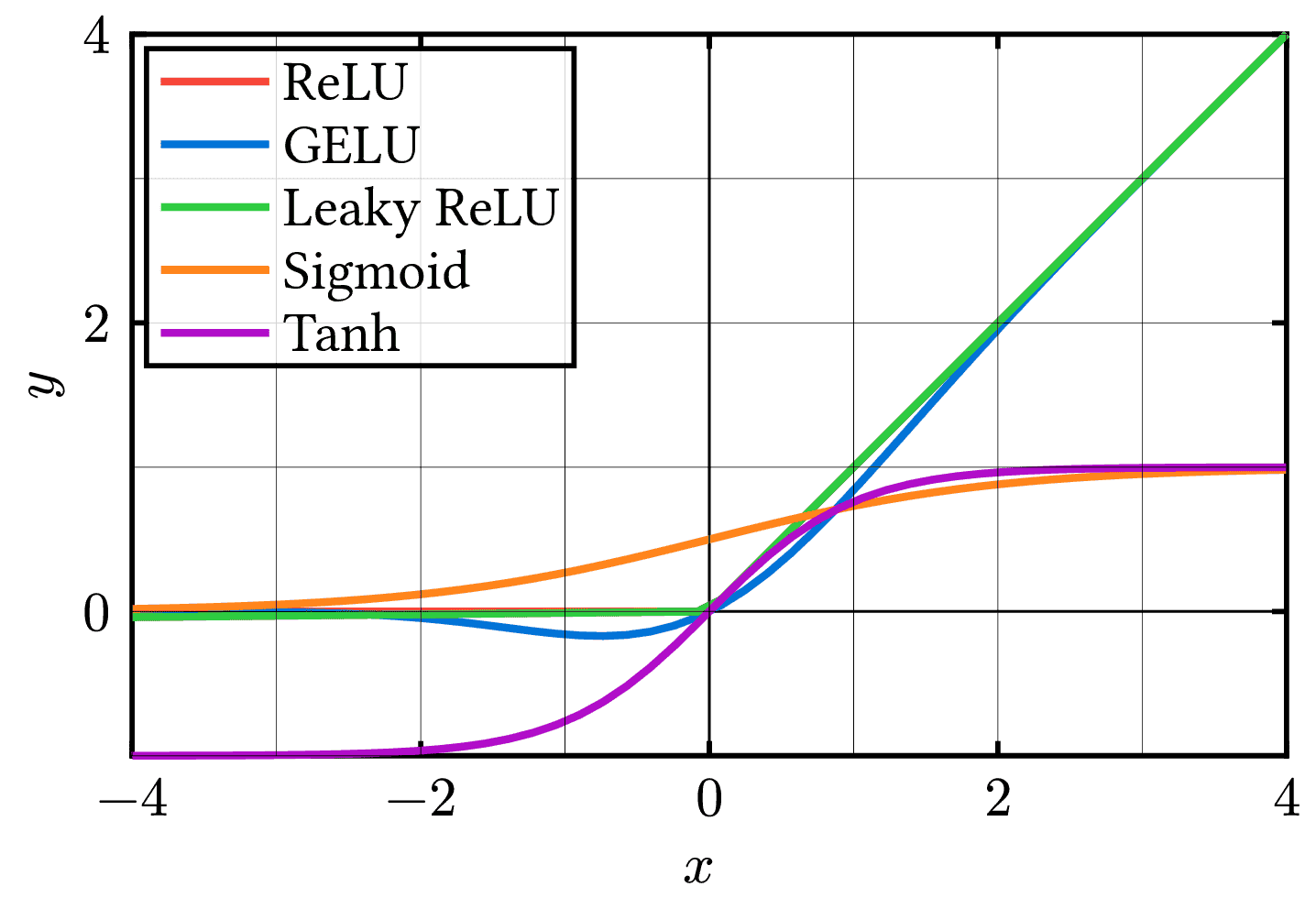
Plot of common machine learning activation functions. Includes the Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU), Gaussian Error Linear Unit (GELU), Leaky ReLU, Sigmoid, and Hyperbolic Tangent (tanh) activation functions. Activation functions introduce non-linearity into neural networks, enabling them to learn complex patterns and relationships in data. The choice of activation function can have a significant impact on the performance and convergence of a neural network. ReLU is widely used due to its simplicity and ability to alleviate the vanishing gradient problem. GELU and Leaky ReLU are variants of ReLU that address some of its limitations. Sigmoid and tanh are classical activation functions that squash the input to a fixed range, but they are less commonly used in modern deep learning architectures due to the vanishing gradient problem.
Edit
Download
Code
ml-activations.tex (45 lines)
#import "@preview/cetz:0.2.2": canvas, plot, draw
#let vector(v) = $bold(#v)$
#set page(width: auto, height: auto, margin: 3pt)
#let relu(x) = if x < 0 { 0 } else { x }
#let gelu(x) = 0.5 * x * (1 + calc.tanh(calc.sqrt(2 / calc.pi) * (x + 0.044715 * calc.pow(x,3))))
#let leaky_relu(x) = if x < 0 { 0.01 * x } else { x }
#let sigmoid(x) = 1 / (1 + calc.exp(-x))
#let tanh(x) = (calc.exp(x) - calc.exp(-x)) / (calc.exp(x) + calc.exp(-x))
#let size = (8, 5)
#canvas({
plot.plot(
size: size,
y-tick-step: 2,
x-tick-step: 2,
legend: "legend.inner-north-west",
legend-style: (item: (spacing: 0.18)),
{
plot.add-hline(0, style: (stroke: 0.5pt))
plot.add-vline(0, style: (stroke: 0.5pt))
for (key, (func, color)) in (
"ReLU": (relu, red),
"GELU": (gelu, blue),
"Leaky ReLU": (leaky_relu, green),
"Sigmoid": (sigmoid, orange),
"Tanh": (tanh, purple)
).pairs() {
plot.add(style: (stroke: color + 1.5pt), domain: (-4, 4), func, label: key)
}
}
)
draw.grid((0,0), size, stroke: 0.1pt)
})
// #box(width: 30em)[
// Popular ML activation functions.
// $"ReLU"(vector(x)) = vector(x)^+ = max(vector(x), 0)$ is the most widely used activation function in deep learning due to its simplicity and computational efficiency.
// $"GELU"(vector(x), mu=0, sigma=1) = vector(x) / 2 (1 + op("erf") (vector(x) \/ sqrt(2)))$ is a differentiable variant of ReLU.
// $"Leaky ReLU"(vector(x)) = max(0, vector(x)) + alpha dot min(0, vector(x))$ with $alpha < 0$ is a variant of ReLU that adds a small gradient for negative activations.
// $"Sigmoid"(vector(x)) = (1 + exp(-vector(x)))^(-1)$ smoothly squashes the input to the range (0, 1).
// $"Tanh"(vector(x)) = (exp(vector(x))+exp(vector(−x))) / (vector(exp(x))−exp(vector(−x)))$ is a scaled and shifted version of the sigmoid function.
// ]