k-Space
Tags
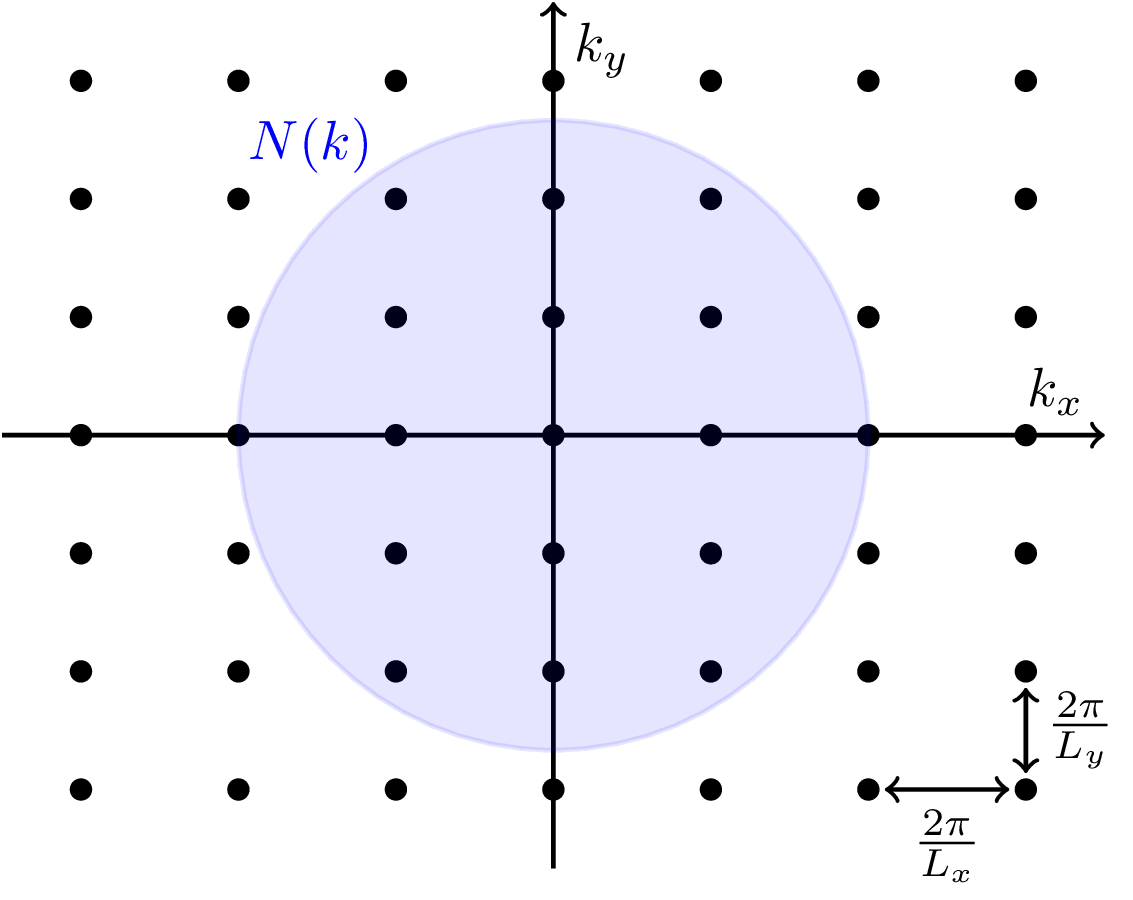
The -space region of wave vectors up to a given magnitude is a disk of area . The -space area occupied by a single particle state is
where the factor of is due to the spin degeneracy . The number of states with wave vector magnitude smaller than is
-space is used extensively in solid state physics e.g. to visualize the energy bands of a material as a function of electron momentum. In position space, the position-energy dispersion would just be a probability blur.
Edit
Download
Code
k-space.tex (27 lines)
\documentclass[tikz]{standalone}
\begin{document}
\begin{tikzpicture}[thick]
% Dot grid
\def\xrange{3}
\def\yrange{3}
\def\ratio{3/4}
\foreach \x in {-\xrange,...,\xrange}
{\foreach \y in {-\yrange,...,\yrange}
{\fill (\x,\ratio*\y) circle[radius=2pt];}}
% Axes
\draw[->] (-\xrange-1/2,0) -- (\xrange+1/2,0) node[above left] {$k_x$};
\draw[->] (0,-\ratio*\yrange-1/2) -- (0,\ratio*\yrange+1/2) node[below right] {$k_y$};
% Lattice spacing
\draw[<->,shorten >=3,shorten <=3] (\xrange-1,-\ratio*\yrange) -- (\xrange,-\ratio*\yrange) node[midway,below] {$\frac{2 \pi}{L_x}$};
\draw[<->,shorten >=3,shorten <=3] (\xrange,-\ratio*\yrange) -- (\xrange,-\ratio*\yrange+\ratio) node[midway,right] {$\frac{2 \pi}{L_y}$};
% Circle
\draw[blue,fill=blue,fill opacity=0.1] (0,0) circle (2/3*\yrange);
\node[blue] at (130:2.4) {$N(k)$};
\end{tikzpicture}
\end{document}